New Chinese archaeological discoveries were announced in 2024. The Xiatang site of Xianju County, Zhejiang, and the No. 1 Tomb of Wuwangdun, etc. were selected. Today (February 19), the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences announced six "New Chinese Archaeological Discoveries in 2024", namely: Dadong Site in Helong City, Jilin, Xiatang Site in Xianju County, Zhejiang, Majiayao Cultural Settlement in Siwa Site in Lintao County, Gansu, Zhouyuan Site in Baoji City, Shaanxi, Wuwangdun, Huainan City, Anhui, and Yuan, Ming and Qing porcelain making sites in Jingdezhen City, Jiangxi.
In addition, the Monzatipe site in Uzbekistan has been selected as a new archaeological discovery abroad.
Dadong Ruins
Artificial stone sculptures were discovered around 17,000 years ago
Dadong Ruins in Helong City, Jilin are currently the largest late Paleolithic wilderness site in Northeast Asia. From 2021 to 2024, the Jilin Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology and several units carried out active archaeological excavations of the site.
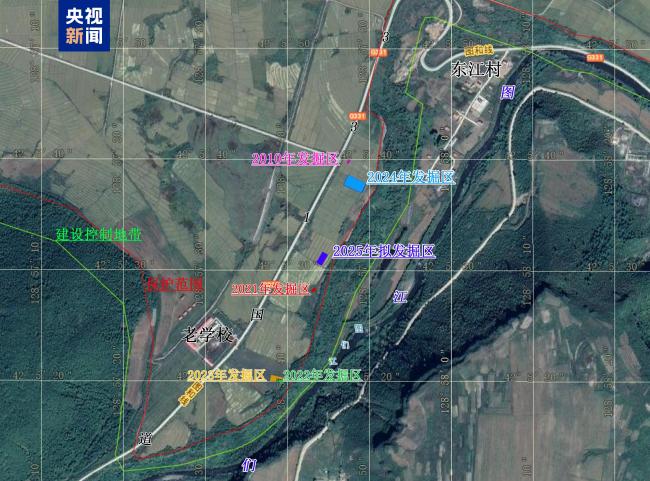
△Schematic diagram of the excavation area of the Dadong Ruins over the years
In the strata that dates from 17,000 to 15,000 years ago, the archaeological team discovered a scratched stone product with a "V" shape, and preliminarily judged that this stone product should be an artificial stone sculpture. According to reports, in the research on the origin and spread of modern human behavior, the relics with scratches are often regarded as one of the important characteristics of proving "behavioral modernity" and are even used as evidence of the emergence of language. Combining the various discoveries of this site, it shows that the Changbai Mountain area of my country plays an important role in the evolution and migration and diffusion of ancient humans in Northeast Asia.
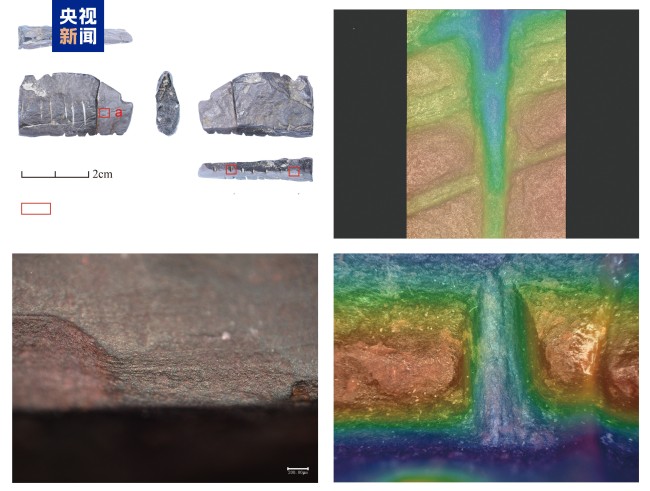
△Hematite Ore Carving
Xiatang Site
Show the social appearance of early rice farming in my country
data-source="cke">As of 2024, Zhejiang Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology and other units have discovered trenches, artificial soil platforms, house sites, food processing sites, and "plazas" of braised soil at the Xiatang Neolithic site in Xianju County, Zhejiang. After comprehensive research, the archaeological team initially restored the structural layout of Xiatang's ancient village, which was a major breakthrough in the social organizational structure of early rice farming agriculture in my country.
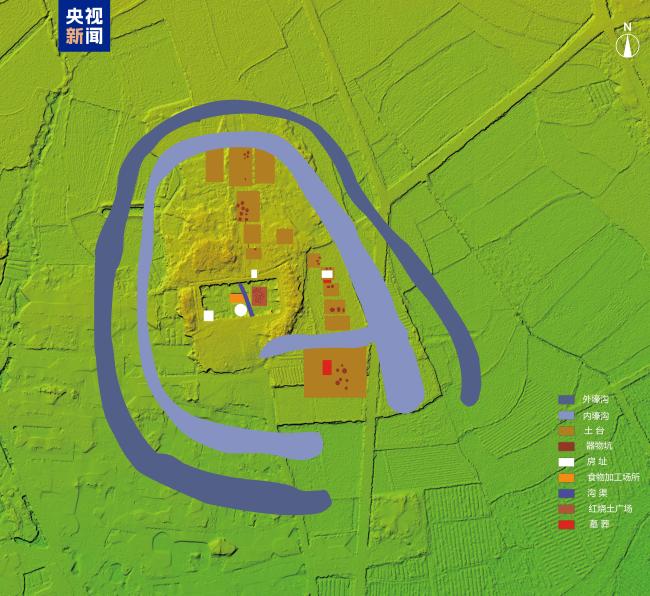
△Schematic diagram of the restoration of the Shangshan cultural settlement in Xiatang site